Research Interests:
The David Lab’s research interests are found at the interface of chemistry and biology, and focus on investigating DNA repair. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) such as the hydroxyl radical, produced by numerous sources in the environment, are known to cause mutation in DNA, thus nature has evolved complex machinery that works in concert to excise and repair damaged nucleobases like 8-oxoguanine (8-OG).
Sources of DNA-Damaging ROS
We are interested in studying glycosylase DNA repair enzymes, such as MutY, MUTYH, and NEIL, that are part of the Base Excision Repair (BER) pathway. The GO Repair Pathway, which is part of BER, helps to regulate mutations resulting from oxidative damage product 8-OG in DNA. Glycosylases involved in these pathways, such as MutY, locate and cleave mismatched nucleobases which arise from oxidative DNA damage, triggering a repair process that is critical to an organism’s survival. The David Lab seeks to determine how these enzymes locate and remove their specific targets while immersed in a vast sea of naturally occurring DNA in the living cell.
The GO Repair Pathway
MUTYH and Cancer:
The David Lab seeks to explore mechanisms of cancer relating to DNA repair. Mutations to DNA repair proteins can result in dysfunctional DNA repair, allowing for the accumulation of DNA damage and subsequent mutation, leading to destabilization of the genome – a process that can have a devastating impact on a living organism. In fact, inherited biallelic variants of the MutY human homolog MUTYH have been linked to predisposition to tumors in humans in a disease called MUTYH Associated Polyposis (MAP), in a study examining Family “N”.1 A hallmark of this condition is the presence of a significant excess of G:C → T:A transversion mutations in tumors, indicative of a lack of repair by MUTYH. Certainly, the discernment of the mechanism of MUTYH will help reveal new means of treatment for MUTYH-related diseases such as MAP.
Family “N” Pedigree: Siblings with Multiple Colorectal Adenomas and Carcinoma1
NEIL
Unlike most DNA glycosylases which remove one or two DNA lesions from duplex DNA, the Nei-like family of glycosylases (NEIL 1-3) are capable of removing a wide range of different lesions and bulky adducts from DNA, including non-duplex DNA structures such as single strand, bubble, bulge, and G-Quadruplexes DNA. Each NEIL has unique molecular pathway associations and has been shown to play key roles in a large array of diseases including cancer, metabolic, and neurodegenerative diseases. While not fully understood, the NEIL enzymes have a plethora of regulatory functions to help maintain genome stability. Our lab uses a combination of chemical, biochemical, and cellular work to better understand the underpinning complexities associated with NEIL mediated repair.
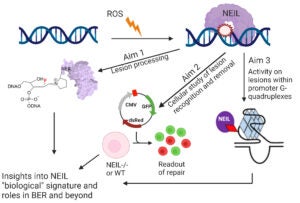
Overall NEIL Research Aims
Tools of the David Lab:
We employ numerous tools of chemical biology to reveal mechanistic and structural details of the BER pathway. Chemical modification of DNA yields synthetic mimics of naturally existing DNA that are subjected to numerous in-vitro or cellular assays, helping to gain insight into DNA repair enzymes such as MutY and MUTYH. Binding and kinetics assays are employed to determine enzymatic details such as binding efficiency and reaction coefficients of proteins like MutY, MUTYH, and NEIL. Fluorescence spectroscopy and electrochemistry are utilized to assess the role of enzyme cofactors and determine their essential function in DNA repair. Numerous biological assays, such as RIF and GFP assays, help to analyze the consequences of enzyme variants and substrate profiles on proteins like MutY and MUTYH. Also, we explore novel repair mechanisms of established enzymes when acting in the presence of damaging chemicals, such as oxidizing or methylating agents. The many tools of the David Lab will offer new insight into DNA repair mechanisms, and will result in new and improved methods of examining DNA repair enzymes.
Research Funded By:


David Lab FYI Video Archive
How to efficiently pour column fractions: Run a column <60 min.
Doing this will greatly increase your already-existing love of columns. And your productivity.
Get the most out of your flash column. It’s not called slow column chromatography.
Video by Robert Van Ostrand.
1.) Al-Tassan, N.; Chmiel, N. H.; Maynard, J.; Fleming, N.; Livingston, A. L.; Williams, G. T.; Hodges, A. K.; Davies, D. R.; David, S. S.; Sampson, J. R.; Cheadle, J. P., Inherited variants of MYH associated with somatic G:C→T:A mutations in colorectal tumors. Nat. Genet. 2002, 30 (2), 227-232.
Keywords: #DavidLab #TheDavidLab #UCDavis #DNA #DNARepair #Muty #Mutyh #8OG #enzymes #ModifiedOligonucleotides #ModifiedNucleosides #OrganicSynthesis #Synthesis #BaseExcisionRepair #BER #NEIL #ChemicalBiology #Chemistry #SheilaDavid #UCDavisChemistry #glycosylase #DNARepairUCDavis



