Recent Article Published by the David Lab at UC Davis:
The DNA repair enzyme MUTYH potentiates cytotoxicity of the alkylating agent MNNG by interacting with abasic sites
Journal of Biological Chemistry
Inherited defects in the DNA repair gene MUTYH lead to cancer, proof that MUTYH has a critical role in preventing cancer in normal cells. In a new study from the David Lab, MUTYH is shown to have a new role that implicates it in the response to a common class of chemotherapy drugs, alkylating agents (https://www.jbc.org/content/early/2020/01/30/jbc.RA119.010497).
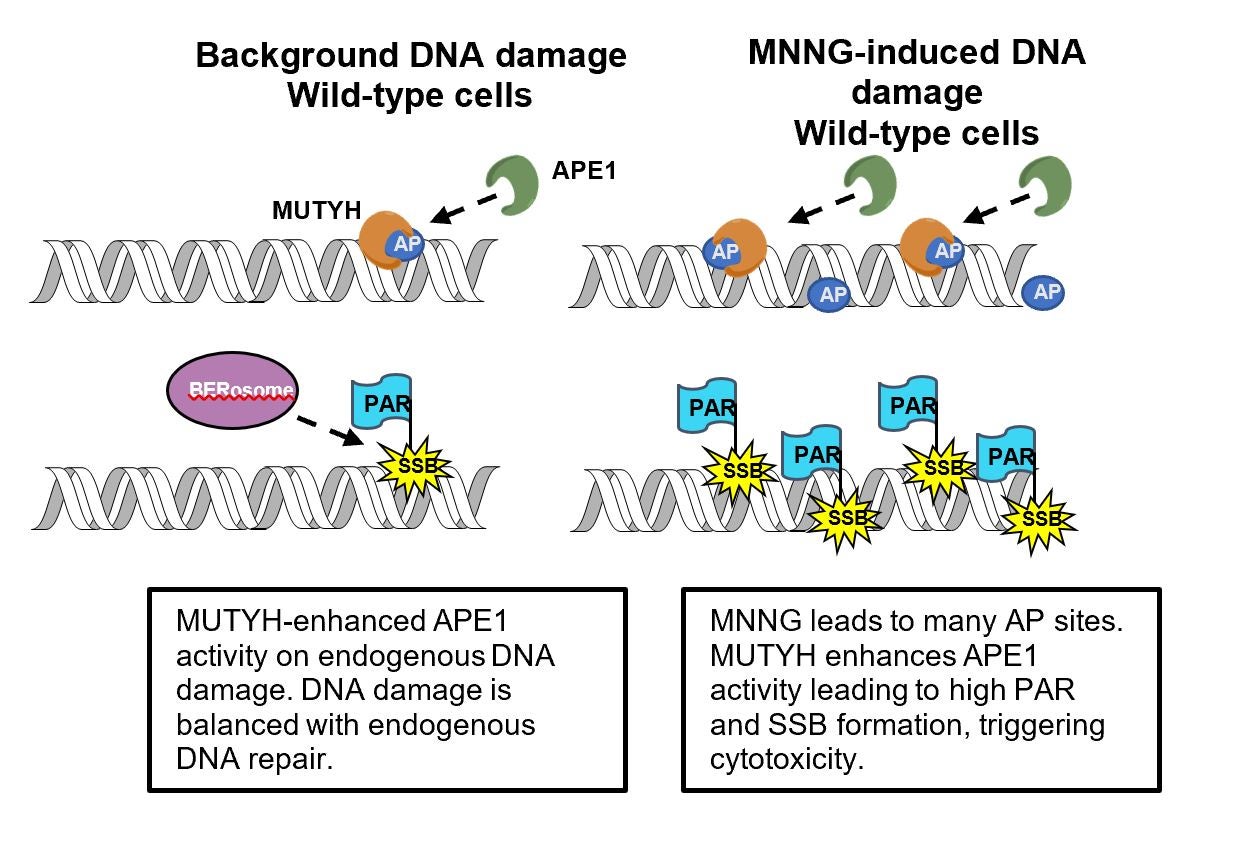
Cancer cells evolve resistance to chemotherapy drugs by a number of mechanisms, including upregulating DNA repair enzymes such as BRCA1, which helps cancer cells survive DNA damaging chemotherapy agents. Surprisingly, MUTYH does not help repair alkylating agent DNA damage, but instead enhance alkylating agent toxicity. This study uncovers the underlying molecular mechanism of this activity, which involves MUTYH stimulating cells to create more toxic DNA repair intermediates. By uncovering the molecular mechanism, this research suggests that MUTYH has both a role in preventing DNA mutations that cause cancer, and a separate role in helping kill cancer cells that are treated with chemotherapy drugs, thus the loss of MUTYH is a “double-whammy”. Tests to determine if cancer patients have normal versus functionally-deficient MUTYH may alter chemotherapy treatment choices if these results can be generalized to clinical practice.
Citation:
Raetz, A.G.; Banda, D.M.; Ma, X.; Xu, G.; Rajavel, A.N.; McKibbin, P.L.; Lebrilla, C.B.; David, S.S. The DNA repair enzyme MUTYH potentiates cytotoxicity of the alkylating agent MNNG by interacting with abasic sites. J. Biol. Chem. 2020.
Keywords:
#sheiladavid #davidlab #mutyh #thedavidlab #ucdavischemistry #cytotoxicity #alkylatingagent #mnng #dna #dnarepair #muty #ucdavis #chemistry #biologicalchemistry #chembio #journalofbiologicalchemistry
