The Annual R. Bryan Miller Symposium at UC Davis brings top speakers from the field of chemical biology to share cutting edge research results and perspectives on the future of chemical biology research. Dr. Sheila David is the Miller Symposium Committee Chair, and directs the event with the support of faculty, staff, and students. The David Lab attended the 2019 Miller Symposium at UC Davis in full force.
This year’s theme of the Miller Symposium was “Chemistry and Biology of Pain,” and included speakers such as Justin DuBois of Stanford, Alanna Schepartz of Yale, Jon Sack of UC Davis, Ann Weber of Kallyope & Merck, and more.


Chandrima Majumdar of the David Lab played a significant role in supporting and organizing the event, and received recognition for her contribution at the awards ceremony.

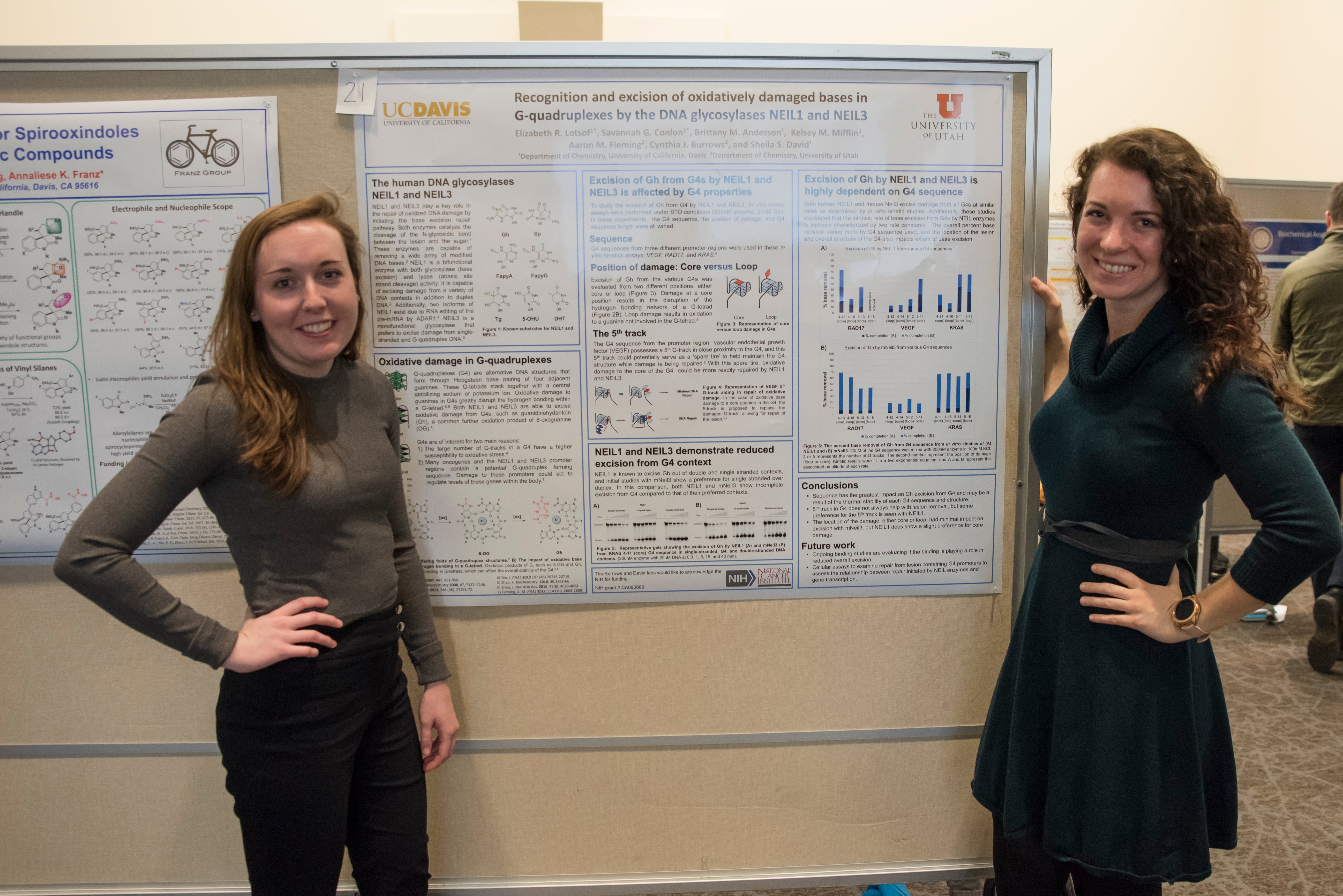
The Miller Symposium also includes a poster session where researchers present their latest findings. Liz Lotsof and Savannah Conlon of the David Lab shared their work at the poster session, which involves DNA glycosylases NEIL1 and NEIL3 and their ability to recognize and excise oxidative damage located in G-quadruplexes.
Undergraduate Researcher Madeline Bright of the David Lab won the 2019 Francesca Miller Undergraduate Research Award for her work involving the synthesis and duplex stability analysis of previously unreported and rationally designed modified oligonucleotides developed to act as substrates for DNA repair protein MutY in enzyme assays utilized by the David Lab. The modified oligonucleotides synthesized in this project will help elucidate the target recognition mechanism of MutY. Madeline has been a member of the David Lab since January 2018 and works with 3rd year PhD student Robert Van Ostrand. Congratulations Maddy!
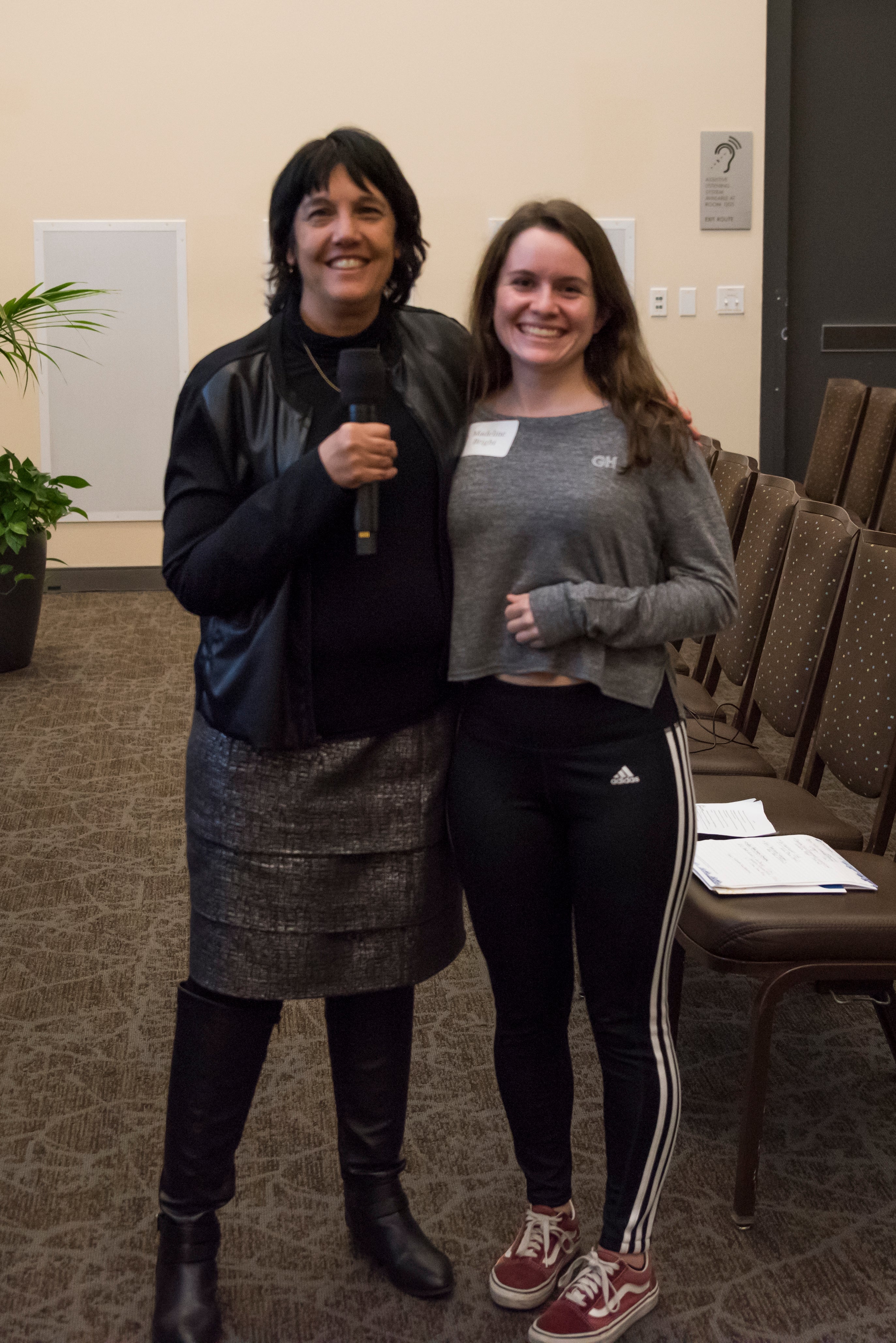
The David Lab @ Miller 2019

Thank you to Jackson Zhu for taking the photos.
Keywords:
#MillerSymposium #UCDavis #ChemicalBiology #DNARepair #DavidLab #SheilaDavid #UCDavisChemistry

