New Manuscript Published: The Zinc Linchpin Motif in the DNA Repair Glycosylase MUTYH: Identifying the Zn2+ Ligands and Roles in Damage Recognition and Repair.
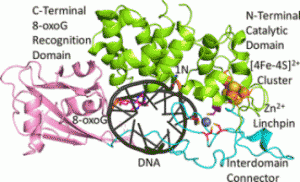
A recent publication from the David, Siegel and Lim (Academia Sinica, Taiwan) labs (Nuñez et al., JACS, 2018) provides insight into the coordination sphere and critical role of a Zn2+ metal binding site in the DNA repair glycosylase MUTYH. Genome database mining and sequence alignment of MUTYH orthologs, along with computational modeling, identified and supported Zn2+ ligation by four Cys residues. Three of the Cys residues lie in an interdomain connector region unique to mammalian MutY enzymes, while the 4th Cys is located in close proximity to the Fe-S cluster DNA binding domain. The functional consequences of reduced Zn2+ chelation on MUTYH-mediated DNA repair activity evaluated using a battery of in vitro and cell-based assays revealed the importance of Zn-coordination in recognition of the damaged DNA substrate. The critical nature of the “Zinc Linchpin Motif” suggests additional functions unique to higher organisms in damage signaling and crosstalk with other DNA repair pathways.
More information at https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.8b06923.
Source:
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 13260-13271.
Keywords: #Muty #Mutyh #BER #DNA #DNARepair #ZincLinchpinMotif #Zn2+ #8OG #DavidLab #UCDavis

